Schleich Test Technologies
Partial discharge testers with surge voltage
Everything you always wanted to know about partial discharge and surge voltage.
The partial discharge test, often also called “PD test” or “PD test” in English, is one of the most important and meaningful test methods today, together with the surge voltage test, for reliably detecting problems in windings. It mercilessly uncovers a large number of insulation, material and production faults.
Why is the partial discharge test so important?
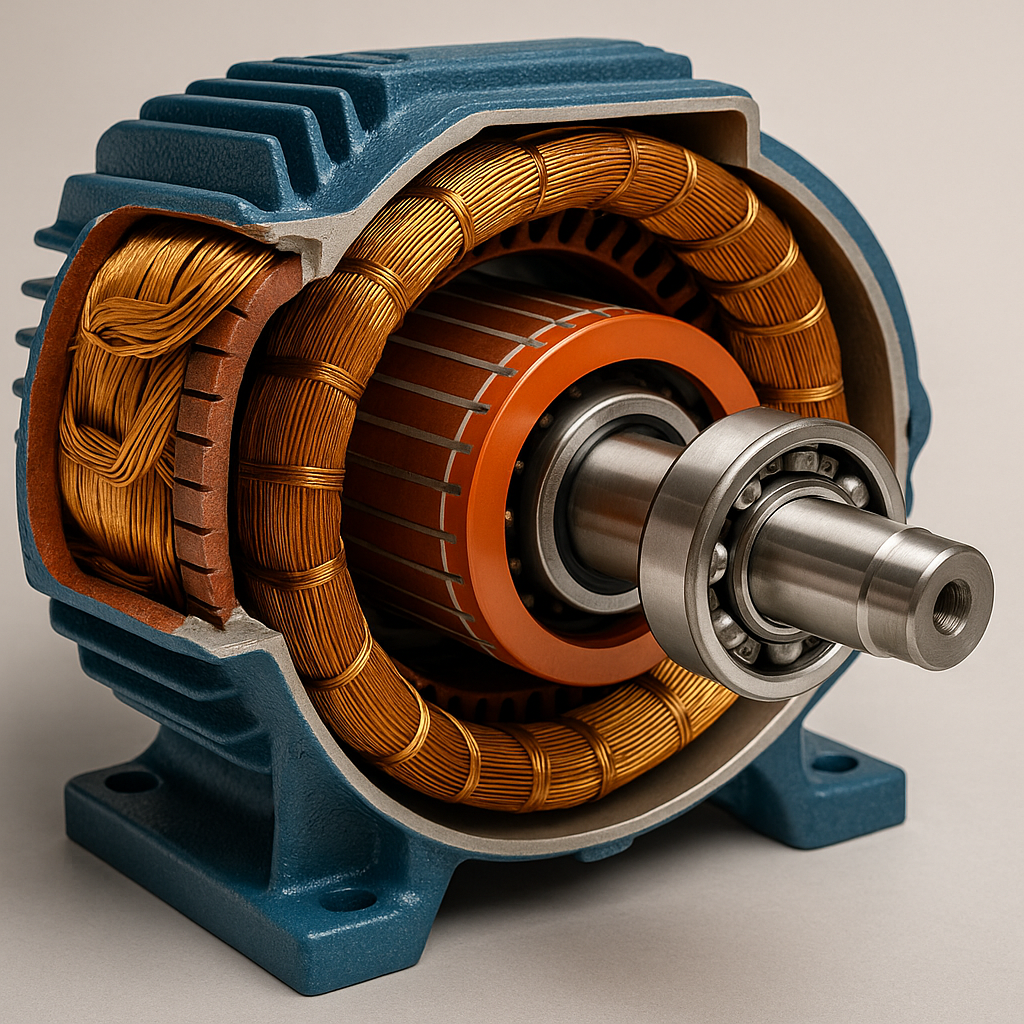
Electric motors, generators, rotors, stators, transformers, valve coils, winding goods of all kinds and others can only be operated safely and for a long time if they have high electrical insulation strength, good material quality and flawless manufacture. Poor insulation quickly leads to total failure.
With the partial discharge test in combination with the surge voltage test, you determine the quality of the winding and the insulation system inside the winding , but also for the laminated core.
SCHLEICH has developed an extensive portfolio of test devices from 1,000 to 15,000 V to cover almost all areas of testing coiled goods with the partial discharge test.
Of course, the partial discharge test cannot replace all known test methods. Therefore, in most cases, a test device / test machine consists of a combination of different test methods.
The starting point is always the surge voltage test - and this is best done in combination with the PD test.
Where is the test object tested?
The surge voltage test is the "deep look into the winding" .
- within the winding from turn to turn
- from coil to coil
- from phase to phase
- from winding to laminated core
Does this also work with a high-voltage test? No!
In no case can such a depth of testing be achieved with the high-voltage test.
And the non plus ultra is the surge voltage test in combination with the partial discharge test.
Which faults does the partial discharge test reveal in addition to the surge voltage test ?
- Poor frequency converter suitability
- Insulation distances too small
- poorly placed phase separators
- insulation weaknesses
- Enamelled copper wire fault
- Spacing problems between turns with high potential difference
- Spacing problems between phases
- Distance problems to the laminated core
- Spacing problems between layers
- and more
How does the partial discharge test work technically?
In principle, the surge voltage tester generates a high-voltage pulse with a very high edge steepness.
To do this, it charges the surge capacitor integrated in the test device to the desired voltage level. As soon as the test voltage is reached, the test device switches the charged capacitor to the winding to be tested via a very fast semiconductor switch.
This results in an oscillating circuit consisting of the inductance of the test object and the charged capacitor. The impulse response on the oscillating circuit is a very steep increase in voltage followed by the typical voltage curve in the form of a damped oscillation.
If there are defects of the type described above, a high-energy lightning discharge does not always have to occur when higher test voltages are applied.
However, if the partial discharge inception voltage is exceeded, partial low-energy discharges can occur at the damaged point. These are neither visible nor audible. However, they often lead to a total failure of the insulation in a short space of time.
Partial discharge can also be referred to as pre-discharge, since it occurs even at low test voltages. So they are a kind of “harbinger” of impending damage.
This is exactly what makes the partial discharge test so interesting and important.
How is the partial discharge test carried out?
Partial discharge is a side effect of AC high-voltage testing and/or surge testing.
Since an electromagnetic wave is emitted with every electrical discharge, the partial discharge can be easily received with an antenna.
This is ideally possible with open windings. So whenever the winding is not encased in metal as in a fully assembled motor/generator.
Since the PD also spreads to the connection lines of the test object, the PD can alternatively be measured with a coupling module for windings that are completely shielded with metal.
Requirements for a partial discharge test device for winding systems?
SCHLEICH partial discharge testers typically have the following features:
- standard test
- Surge voltage pulses high rate of voltage rise
- very fast measurement technology with high resolution
- Determination of
- inception voltage
- repetitive inception voltage
- repetitive intermittent voltage
- extinction voltage
- fully automatic analysis
- Fully automatic switching between the different winding connections of the test object
- Development, production and service - Made in Germany
SCHLEICH surge voltage/partial discharge test devices are based on over 30 years of experience and pioneering work. From the beginning, the measurement technology was not analog but always digital. In principle, the latest technologies are always used.
How do you find the right partial discharge tester?
If you only want to carry out partial discharge tests on your test object, you are well advised to use a single test device. It contains the surge voltage test as a starting point for determining the partial discharge.
If the test object also requires further tests, we recommend our combination test devices/multifunction testers. Additional test methods such as partial discharge, AC high-voltage test – plus partial discharge if required, ohmic resistance test, rotary field test, etc. can be integrated here. The fully automatic test method switchover ensures that no measuring lines on the test object have to be reconnected manually during the test.
Thanks to the intuitive and convenient operation of our surge voltage testers, each test is carried out quickly, precisely and cost-effectively.
The SCHLEICH product portfolio
- Surge voltage from 1,000 V up to 50,000 V
- Partial discharge from 1,000 V up to 15,000 V
- Can be expanded with any additional test method required
- Standardized interfaces such as RS 232, Ethernet / LAN, USB for PC communication
- 24 V digital I/O for PLC communication
- Expandable to Industrial Ethernet and fieldbus systems for PLC communication
- Almost unlimited storage space for test plans and test results
- All parameters are determined via the software
In addition, we are happy to plan, design and produce individually tailored solutions for you:
- Single tester, combination tester, multifunction tester
- Test machines/test systems with relay matrix (2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12 … 100 terminals)
- laboratory places
- test workstations
- Production lines with transfer systems
- EOL Jobs
- large plants
When selecting your surge voltage/partial discharge test device, also pay attention to the “soft skills” of the provider. We offer all the necessary accessories and accompany you throughout the service life of your surge voltage/partial discharge tester:
- Professional advice with technical know-how
- Careful initial start-up
- Regular certified calibration
- After-sales support from our service team
- Service on the phone or on site
- Tailored training